When a business uses FIFO, the oldest cost of an item in an inventory will be removed first when one of those items is sold. This oldest cost will then be reported on the income statement as part of the cost of goods sold. Specific inventory tracing, also known as the specific identification method, is the most involved and time-consuming method of all four since it involves using the actual COGS for each product sold. It can only be used when you know the price of all components of a product and can trace their costs. Average cost valuation uses the average cost of all your batches to determine the COGS for each unit. Compared to FIFO and LIFO, it is slightly easier since you’ll use the same COGS calculation for each unit sold.

FIFO method and inventory valuation

It takes less time and labor to implement an average cost method, thereby reducing company costs. The method works best for companies that sell large numbers of relatively similar products. Last in, first out (LIFO) is another inventory costing method a https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc company can use to value the cost of goods sold. Instead of selling its oldest inventory first, companies that use the LIFO method sell its newest inventory first. In some cases, a business may not actually sell or dispose of its oldest goods first.
What is the FIFO method in accounting?

It makes sense in some industries because of the nature and movement speed of their inventory (such as the auto industry), so businesses in the U.S. can use the LIFO method if they fill out Form 970. The store purchased shirts on March 5th and March 15th and sold some of the inventory on March 25th. The company’s bookkeeping total inventory cost is $13,100, and the cost is allocated to either the cost of goods sold balance or ending inventory. Two hundred fifty shirts are purchased, and 120 are sold, leaving 130 units in ending inventory. Before diving into the inventory valuation methods, you first need to review the inventory formula.
Inventory values when all units are sold
One is the standard way in which purchases during the period are adjusted for movements fifo formula accounting in inventory. The second way could be to adjust purchases and sales of inventory in the inventory ledger itself. The problem with this method is the need to measure value of sales every time a sale takes place (e.g. using FIFO, LIFO or AVCO methods). If accounting for sales and purchase is kept separate from accounting for inventory, the measurement of inventory need only be calculated once at the period end.
- The first in, first out (FIFO) cost method assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first, while the last in, first out method (LIFO) states that the newest items are sold first.
- Consult an accounting professional to ensure the transition is handled properly.
- Besides calculating COGS, you can use the FIFO accounting method to calculate the value of your remaining (unsold) inventory, also known as inventory valuation.
- Learn about emerging trends and how staffing agencies can help you secure top accounting jobs of the future.
- Let’s say that a new line comes out and XYZ Clothing buys 100 shirts from this new line to put into inventory in its new store.
Industry, regulatory and tax considerations
Because the brand is using the COGS of $5, rather than $8, they are able to represent higher profits on their balance sheet. Adopting the FIFO method aligns with accounting best practices under GAAP (generally accepted accounting principles). FIFO inventory accounting leads to financial reporting that reflects the true liquidation value of inventory assets. Overall, embracing FIFO supports transparency and accuracy in financial analysis. Since older inventory costs are typically lower due to inflation, COGS under FIFO is lower.

Comparative Analysis: FIFO vs. LIFO and Weighted Average
- However, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) permits firms to use FIFO, but not LIFO.
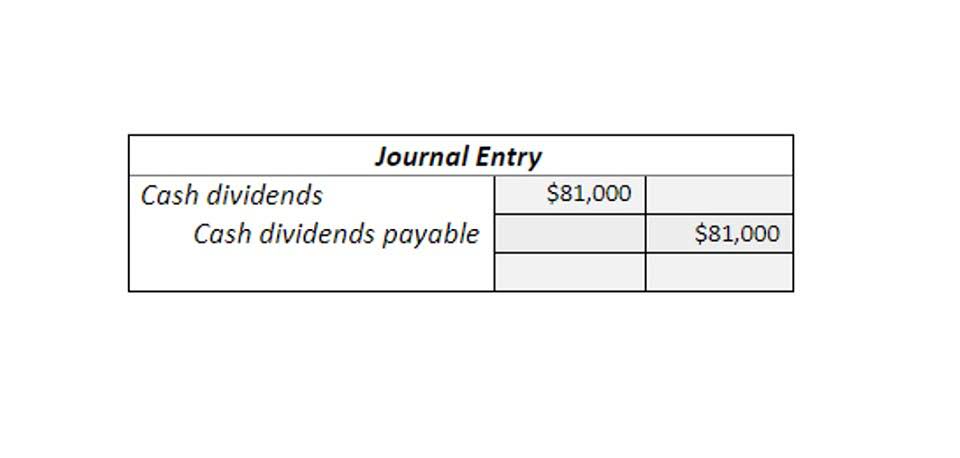
- This means that you generated $1,630 of profit by selling 110 candles.
- The first guitar was purchased in January for $40.The second guitar was bought in February for $50.The third guitar was acquired in March for $60.
- The LIFO method is helpful for businesses whose prices are more subject to inflation, like grocery stores, convenience stores, and pharmacies.
This impacts financial KPIs like net income and asset valuation for analysis. However, the inventory accounting differences between FIFO and LIFO mean that FIFO typically results in higher taxable income. So while FIFO may improve financial reporting metrics, it can also increase a company’s income tax burden. The FIFO (First In, First Out) method is a fundamental concept in financial accounting and inventory management. It refers to the practice of tracking inventory flows and assigning costs on the assumption that the oldest goods in a company’s inventory are sold first. Assume a company purchased 100 items for $10 each and then purchased 100 more items for $15 each.
Also, the weighted average cost method takes into consideration fluctuations in the cost of inventory. It does this by averaging the cost of inventory over the respective period. Specifically, you’ll need to calculate the value of unsold inventory to list it as an asset on your balance sheet.
When calculating inventory and Cost of Goods Sold using LIFO, https://www.bookstime.com/ you use the price of the newest goods in your calculations. First, we add the number of inventory units purchased in the left column along with its unit cost. Using the FIFO method makes it more difficult to manipulate financial statements, which is why it’s required under the International Financial Reporting Standards. Depending upon your jurisdiction, your business may be required to use FIFO for inventory valuation. Under this, the average cost per unit is computed by dividing the total cost of goods available for sale.